What is hot-dip galvanizing?
Hot dip galvanizing is a modern and technically advanced process that protects iron and steel from corrosion. The high quality of the protective coating is the result of several special properties of zinc which make it possible to protect the steel in use against rust and damage. The galvanizing process extends the service life of steel components, structures, road barrier poles.
The galvanizing process involves immersing the component in a galvanizing bath at a temperature of 450°C. The compounds of iron and zinc combine to form an unbreakable strong coating. Before galvanizing, the material undergoes a special chemical treatment.
Why it is worth to galvanize:
- This is the best protection against corrosion for many years
- Zinc coating for high mechanical resistance, higher resistance to damage.
- The zinc coating has aesthetic qualities
- Galvanizing is cost-effective and environmentally safe.
Hot dip galvanizing process
Hot dip galvanizing of steel is the most effective and universal method of protecting steel against corrosion. The zinc coating produced on steel components provides an excellent protective barrier between the steel and the corrosive environment. Depending on the thickness of the manufactured zinc coating and the environment in which the product will be used, the protection against corrosion lasts from 10 to even 100 years. Properly conducted hot dip galvanizing process consists of several stages of steel surface preparation of the components to be galvanized up to their immersion in the bath of liquid zinc and formation of the protective iron-zinc coating.
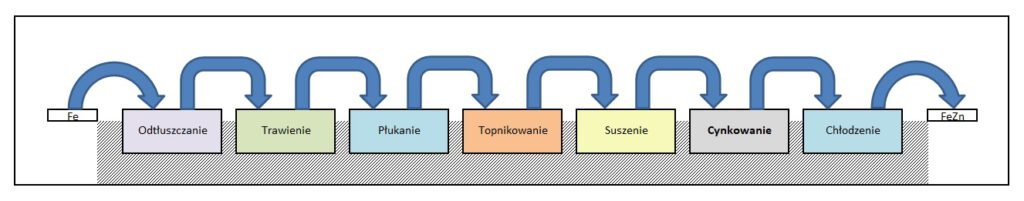
1. Degreasing
The first step in preparing the steel surface for galvanizing is degreasing. The degreasing process is carried out in inorganic alkaline, acidic or neutral solutions. The primary objective of the degreasing process is to obtain a chemically clean surface by removing contaminants such as grease, oil, wax-like substances, etc., which cannot be removed in the subsequent etching step.
2. Etching
The second step of preparing the steel surface for galvanizing is to effectively remove non-metallic substances such as rust, scale and other corrosion products from the surface. The most common and widely used method of etching steel components is a 12-16% hydrochloric acid bath. The bath time depends primarily on the degree of corrosion of the steel components and the concentration of acid in the etching bath.
3. Rinsing
The rinsing process takes place in a bath filled with water. The purpose of this preparation step is to rinse the etched steel components from residual acid. This is to prevent excessive acid transfer into the flux.
4. Fluxing
A very important stage in the process of surface preparation before galvanizing is fluxing. The flux, which is an aqueous solution of zinc chloride and ammonium chloride, is primarily intended to ensure the correct course of the iron-zinc reaction during galvanizing. The flux activates etched and rinsed material surfaces so that they react quickly and evenly with the zinc bath.
5. Drying
The fluxing stage is followed by drying, which takes place in enclosed dryers at temperatures between 100°C and 150°C. This process aims, among other things, at drying out the flux residues and minimizing the temperature difference of the galvanized materialss
6. Galvanizing
The final stage of the hot dip galvanizing process involves immersing previously prepared materials in a bath of liquid zinc at a temperature of 440-460°C. Thanks to the phenomenon of diffusion, i.e. the penetration of zinc atoms into the outer layers of steel, a protective iron-zinc coating is formed. The thickness of this coating depends primarily on the type of steel used and the time in the zinc bath.
7. Cooling
The last stage of the galvanizing process is cooling the galvanized materials in water in order to cool them down to a temperature allowing further processing.

What do we offer in range of hot dip galvanizing?
- expert advice
- many years of experience
- cleaning the material after galvanizing
- unloading and loading
- execution of express orders
- attractive prices
- short lead times
- top quality services
- innovation
- caring for the environment
High temperature hot-dip galvanizing
In June 2020, we commissioned a highly automated process line for applying hot-dip zinc and zinc-aluminium coatings to small parts.
The service is carried out at a temperature of 450-600°C. Galvanizing of small parts takes place in a ceramic bath with dimensions 2000x1100x1500 mm (length/width/height). We also have a crucible furnace for high temperature operation and the application of aluminium and zinc coatings. The line is fully automated, which makes it possible to achieve high efficiency and timely completion of services.
High-temperature hot dip galvanizing is intended for galvanizing steel details, connecting elements, cast iron parts, bolts. After galvanizing, the components are centrifuged in a special centrifuge. This advanced technology eliminates zinc flashes and guarantees the patency of holes and threads. The coating is smooth because the zinc is distributed evenly
High-temperature galvanizing is the best, cheapest and most effective method of corrosion protection. It also protects the details from mechanical damage.









